The sum of any number of terms of a series of values of ![]() is equal to the difference between two values of another function
is equal to the difference between two values of another function ![]() . To find the sum
. To find the sum ![]() , find the function
, find the function ![]() such that
such that ![]() .
.
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[1+2+3+\dots+N=\sum_{x=1}^N \fp{x}{1}=\frac{\fp{x}{2}}{2}\Big|_1^{N+1}=\frac{N(N+1)}{2}\]](https://www.adamponting.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2b5a04b6444f2140e99dcfd3bc6c9af9_l3.png)
![]()
![]()
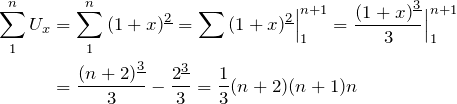
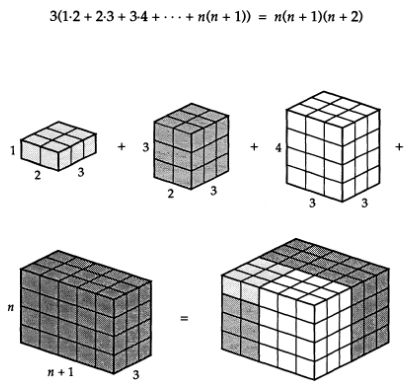
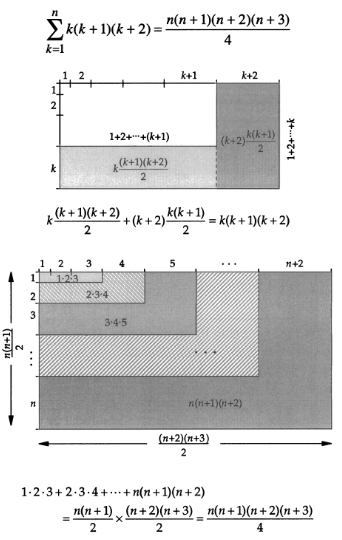
3 pictures of ![]() . The first is (I believe) my own creation.
. The first is (I believe) my own creation.
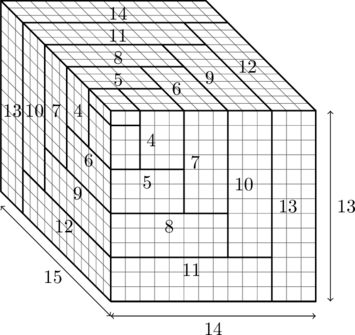
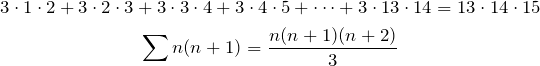
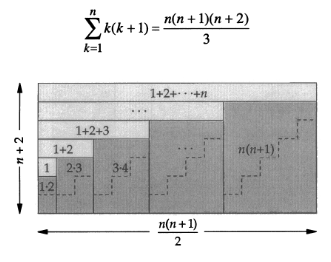
Evaluate ![]()
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[S=\sum_{x=3}^{16} x(x-1)(x-2)=\sum_{x=3}^{16} \fp{x}{3}=\frac{\fp{x}{4}}{4}\Big|_3^{17}\]](https://www.adamponting.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-158c2509ef13ad5d56c8c1a1bb1d030f_l3.png)
![]()
Evaluate ![]()
Using ![]() , with
, with ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() :
:
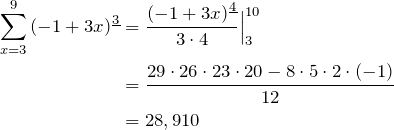
![]()
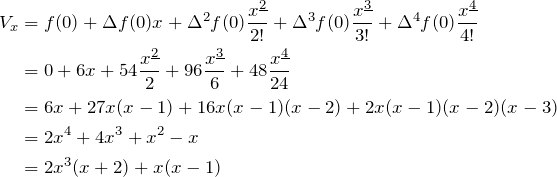
![]()
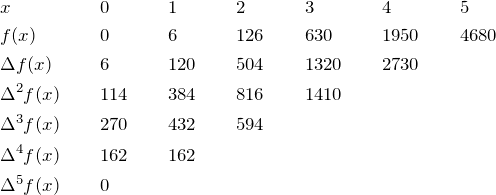
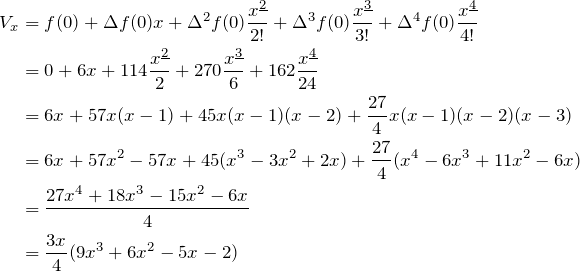
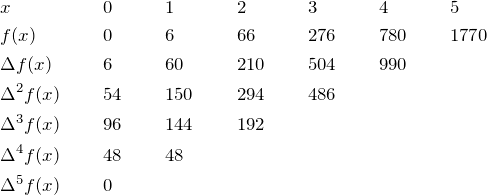
Q. What is the general formula for this type of sum,
![]()
![]() ?
?
![]()
![]()